Average Handle Time: The Ultimate Guide for Contact Centers
Fast food, instant messaging, two-day shipping—consumers crave speed and convenience in every interaction with a business.
And for contact centers, meeting that desire isn’t just a nicety for callers, but a necessity for maximizing efficiency and boosting cost savings across the board.
That’s where understanding Average Handle Time (AHT) comes in. In this guide, we’ll dive deep into call handling—from how to accurately measure AHT, why it’s mission critical for CX, and strategies you can implement to improve it.
Prefer headphones? Take a listen to this post on the Snackable CX podcast.
One
What is AHT and how do you calculate it?
AHT is the average time it takes for your agents to “handle” a customer, or, in other words, to conduct an interaction. It’s a critical KPI because it gauges efficiency and directly influences customer experience AND cost savings.
But there’s a lot of nuance in understanding your contact center’s AHT. Shorter average handle times might look good, but it could also indicate agents racing through calls and not providing a quality experience. Meanwhile, a longer AHT might mean your customers are solving simple questions in self-service channels and agents are left spending more time on the complex questions.
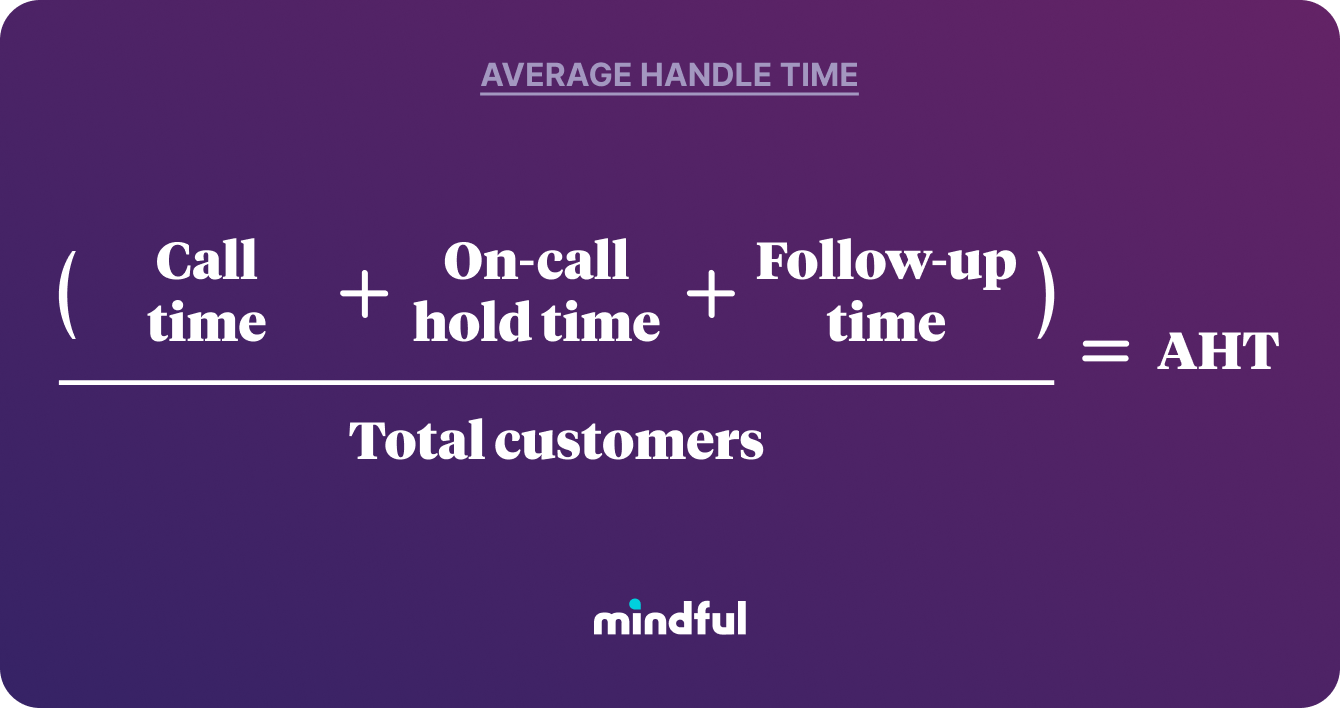
To calculate your AHT, you’ll need to consider agents’ total talk time, total on-call hold time, and total follow-up time. Here’s a quick summary of each one:
- Total talk time: The amount of time an agent spends actively interacting with a customer.
- Total on-call hold time: The amount of time that a customer spends on hold during the actual interaction with an agent—like when the agent puts them on hold to look at their information, or transfers them to another agent or department.
- Total follow-up time: The necessary work that an agent has to complete after interacting with a customer—like taking notes or updating a customer’s information in a CRM.
Next, run all those numbers through the following formula:
Two
Benefits: Improving AHT boosts efficiency and experience.
Improving AHT brings a slough of benefits to both contact centers and customers—improved brand reputation, increased customer satisfaction, better agent morale—but they all boil down to contact center efficiency and customer experience.
1. Tighter AHT leads to contact center efficiency.
Agents that can quickly move through call queues will naturally handle more calls during their shifts, ultimately improving the efficiency of the entire contact center. And when agents are operating at peak performance and taking more calls, workforce managers can use fewer agents to handle the same amount of call volume—directly translating into saved overhead and salary costs.
2. Lower handle time improves customer experience.
A 2021 TCN study found that 59% of customers say their biggest complaint with call centers is the amount of time it takes to resolve an issue. Improving your contact center’s AHT means customers get their questions answered quicker and easier—increasing CSAT and NPS scores across the board.
Three
What is a good AHT for contact centers?
While a good rule of thumb is to keep AHT as short as possible (while still providing a great customer experience), your ideal AHT will depend on the industry you work in and, even more importantly, what customers report when giving you feedback.
Here’s what the AHT looks like across different sectors, according to data from Talkdesk’s 2021 global contact center KPI benchmarking report:
| Industry | Average Handle Time (AHT) |
| Agriculture | 3.50 minutes |
| Consumer/Professional services | 3.55 minutes |
| Financial services & insurance | 4.01 minutes |
| Government & public sector | 4.13 minutes |
| Healthcare | 3.38 minutes |
| Hospitality | 3.11 minutes |
| eCommerce | 3.41 minutes |
| Telecommunications | 2.56 minutes. |
Again, the trick is to find the balance between quickly handling service requests and providing excellent customer support. For this, you’ll need to lean heavily into customer feedback and CSAT data to make sure you’re doing right by your customers.
Three
Three ways to improve AHT
Unlike other metrics, AHT functions independently of agent headcount. You might have a 60% occupancy rate and practically zero hold time for your callers, but, unless your agents can efficiently move through the call queue, your AHT could still ride uncomfortably high.
Improving AHT requires a holistic and a laser-focus approach to implementing the right tech that helps your agents quickly and efficiently handle call queues.
1. Eliminate customer vent time by removing hold times.
Even though the time spent queueing isn’t added to handle time, long hold times obliterate AHT. Because the longer a caller is on hold, the more difficult they are to work with and the more likely they are to vent their frustration to an agent—gobbling up valuable minutes of handle time and leaving your agents feeling major burnout.
The best way to eliminate venting is to kick hold times to the curb. A callback solution lets callers swap hold time for free time by giving them the option of saving their place in line and getting a call when it’s their turn.
And cutting down on AHT using a callback solution isn’t just wishful thinking. We’ve seen some of our own clients shave a whopping 1-2 minutes off of their AHT after implementing Mindful Callback. Over the course of thousands of calls per month, this translates into massive savings and increased customer satisfaction.
2. Prepare agents by collecting intent before the call.
Your agents should act as problem solvers, not data collectors. The more information an agent has about a customer before connecting with them on the phone, the quicker they can diagnose and resolve the issue. And with the right tech, gathering caller information pre-call has never been easier.
Optimize your IVR.
Your IVR configuration can make or break your AHT. Long, drawn-out prompts, confusing or missing menu options, general-que-routing—all of these contribute to customer frustration and unnecessary transfers which add precious handle time to multiple interactions.
The primary purpose of an IVR is to help customers find the help they need as fast as possible. And to accomplish this, an IVR needs to be well balanced in two particular areas:
- Effective routing. Your IVR should ask enough questions to properly route the caller to where they need to go, but avoid asking too many questions so that the caller becomes overwhelmed and frustrated.
- Quick solutions. On one hand, your IVR should highlight self-service options to deflect callers from the contact center. But at the same time, it shouldn’t be so bogged down with self-service options that a caller can’t easily connect with an agent.
For even greater optimization, connect your CRM to your IVR to provide callers with a personalized interaction as soon as their call connects. Phone number and authentication data in your CRM can be used to automatically route callers to the right queue—and trim off some authentication time once the call begins.
Use click-to-call or call scheduling on your website.
Your customers probably looked for an answer on your website before calling into your contact center. By strategically placing a click-to-call (or call scheduler) widget on your website or mobile app, you can collect valuable intent information that will help agents reduce their AHT—while creating a premium experience for customers.
Imagine a customer hitting a digital dead end on your FAQ page. A click-to-call button lets them request a call from the next available agent right from their browser. No more having to navigate the IVR, no more costly and frustrating hold times, and—with a premium solution—an agent can see exactly who they’re talking to and go right into the call with solutions rather than questions, cutting down on AHT from the start.
Connect your chatbot to a call scheduling solution.
Chatbots are great at solving simple problems and self-service tasks. And for more complex issues (the kind that require a human touch), contact centers can use the information collected through a user’s chatbot interaction to help speed along their conversation with an agent.
Rather than losing a user’s digital context if they reach a dead end with your chatbot, use a handoff solution to capture the chat inputs and transcript to route them to the right agent. This removes the process of dialing a support number, going through the IVR, and waiting on hold—removing the typical vent time we mentioned earlier, while supplying your agents with vital information to get the conversation started.
3. Empower agents to handle calls proficiently.
Implementing the right tech is a surefire way to improve AHT in your contact center. But investing in and empowering your agents is also a key piece of the AHT puzzle. Here are a handful of ways you can give your agents what they need to quickly, confidently, and efficiently move through their call queues.
Remove the red tape. Give your agents the leeway and accessibility they need to handle simple tasks without having to transfer calls or escalate to a manager. Look at your call and transfer logs to identify areas or customer queries that result in the most call escalations, then see if there’s an unnecessary hurdle that prevents agents from resolving the call on their own.
Provide training and mentorship. It’s crucial that your support agents feel ready to handle customer requests—especially if they’re new hires. While formal training is always helpful, consider setting up a mentorship program that pairs new hires with experienced agents. You could even set up a quick agent-specific support channel where agents can ask questions and receive help during calls. Comparing AHT between agents—or teams of agents—is a productive way to identify areas where coaching is required or best practices can be established.
Don’t underestimate knowledge databases. Your agents are only as sharp as the tools in their toolbox. An unkempt, difficult-to-navigate knowledge database means agents have to spend more time looking for answers than providing their customers with solutions. Spend time evaluating your knowledge database and surveying your agents to identify specific areas or processes that might need improvement.
Next steps
An optimized contact center and empowered workforce are the keys to improving your AHT and wowing your customers with quick and helpful resolutions.
Make sure to track CSAT while honing your handle times to see if any changes you’re making are negatively impacting the customer experience. And also regularly solicit feedback from your agents to identify areas where they might be feeling burned out (which will ultimately show up in their interactions with customers and spike handle times).
To learn more about how Mindful can help your contact center tighten up its AHT and improve your customer experience, check out our demo to see it in action.
Bonus
Average Handle Time basics and FAQs
What is handle time?
In the contact center, handle time is the total duration of a customer interaction, start to finish. Handle time is an important metric in the contact center because it affects efficiency, customer service quality, and agent productivity. By monitoring and measuring handle time, contact centers can provide better customer experiences and balance efficient interactions with satisfactory resolutions to customer inquiries.
Let’s break down the three main components of handle time:
- Talk time: when the agent is chatting with the customer, answering their questions or addressing their concerns.
- Hold time: the time a customer spends waiting on hold for an available agent or while the agent is getting information or consulting with a supervisor.
- After-Call Work (ACW) Time: After the call, agents may need to update records, prepare for the next call, or document the interaction. The time spent on these tasks is included in the handle time.
What is average handle time?
When someone contacts a customer service center, they want their issue resolved quickly and efficiently. That’s where average handle time (AHT) comes in. AHT shows you the average for how long it takes for an agent to handle a customer interaction. It’s calculated by dividing the total handle time for a specific period by the total number of interactions during that same period.
AHT is a key metric helping measure how well the contact center is handling customer inquiries and how productive its agents are.
How do you calculate average handle time?
Calculating the AHT for a contact center is simple: You just need to add up the total talk time, hold time, and after-call work time for a sample of interactions (the quantity is up to you) and then divide that sum by the number of interactions.
Here’s how to do it:
AHT = (Total Talk Time + Total Hold Time + Total ACW Time) / Number of Interactions
This number tells you the average handle time per interaction and helps you see how efficient your contact center is and how long it takes to handle customer interactions.
What’s a good average handle time?
A good average handle time (AHT) in contact centers depends on factors like industry, the complexity of interactions, and specific goals. Shorter AHT is preferred for simple queries, while longer AHT is needed for technical issues.
AHT targets should be based on customer needs and available resources. Flexibility and adaptability are key in determining a good AHT, as well as an understanding of needs for your lines of business and their respective customers.
How to improve average handle time?
Want to make your contact center more efficient, save costs, and keep customers happy? Here are some helpful ways to improve your AHT:
- Minimize hold time with callback options, self-service options, or alternative channels like live chat or email.
- Train agents well so they can handle inquiries quickly and accurately.
- Use tech like IVR, CTI, and CRM systems to automate tasks and route calls more effectively.
- Optimize call routing and use skills-based assignment to address issues promptly.
- Provide pre-approved scripts and templates for common inquiries to speed up interactions.
- Streamline processes and eliminate redundant steps in agent workflows.
- Monitor agent performance and provide feedback to help them improve.
- Encourage agents to share insights on how to improve processes and customer interactions.
- Introduce gamification elements to motivate agents to improve their performance.
- Continuously assess AHT data, analyze trends, and identify opportunities for further optimization.